Alibaba’s Business Model – How the eCommerce Giant Makes Money
Jack Ma co-founded Alibaba in 1999. It is the world’s largest eCommerce company and is a mashup of Amazon, PayPal, eBay and Google. Alibaba had 1.3 billion active users last year and generated $127.9 billion in revenue in the twelve months ending September 30, 2021. Alibaba is so large it can be hard to keep track of all of its moving parts but here is an overview of three of its core businesses: alibaba.com, tmall.com and taobao.com.
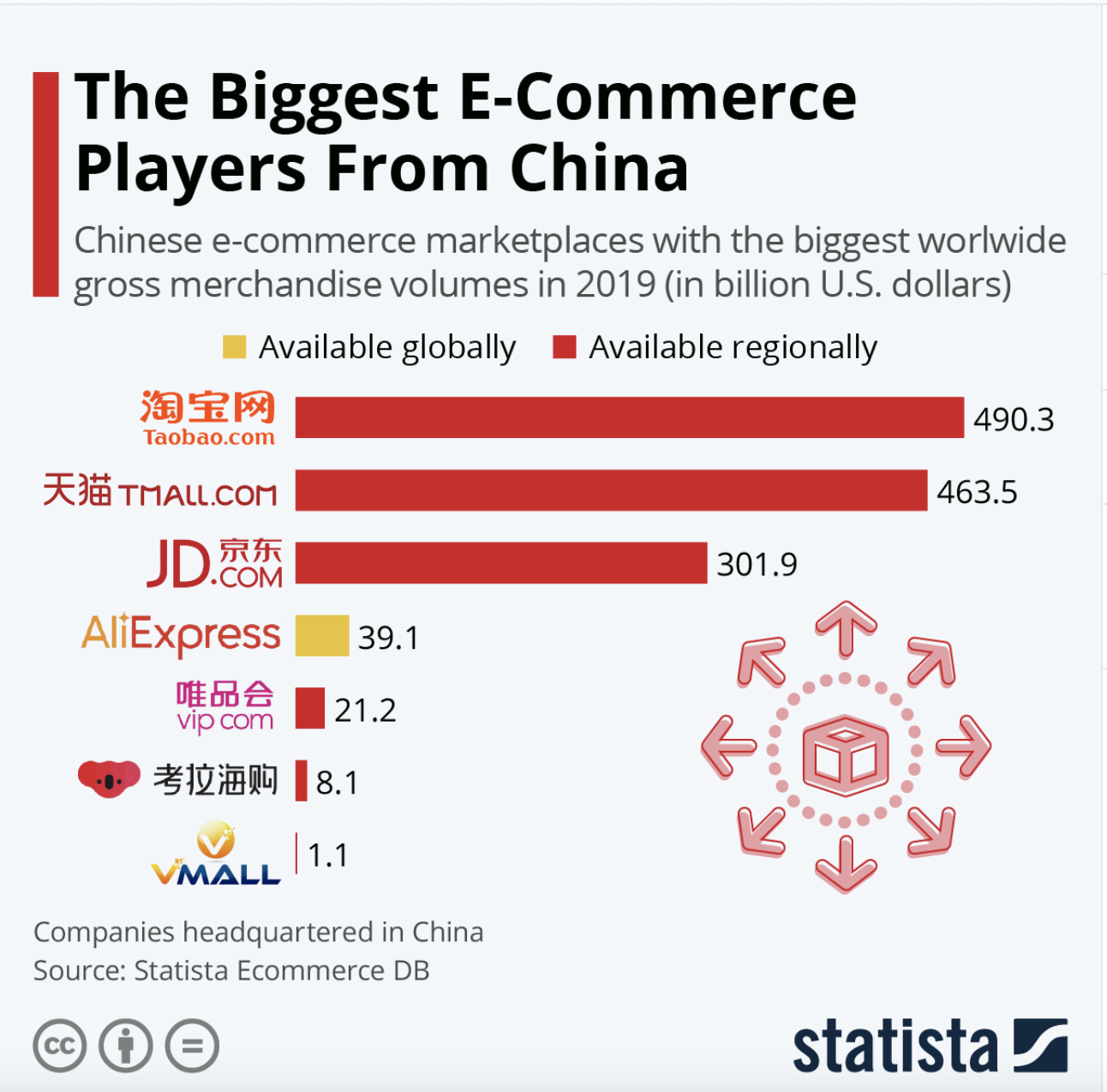
Taobao.com is Alibaba’s biggest website. It is a consumer-to-consumer platform where small businesses and individuals sell items to consumers. It launched in 2003 and provided an opportunity for China’s entrepreneurial class to reach China’s increasingly affluent consumer market. It is similar to eBay in that it connects buyers and sellers but unlike Amazon Alibaba does not own and sell its own inventory. Merchants on Taobao pay a fee to rank higher within the site’s search engine results, similar to the way Google works. Alibaba does not charge merchants on Taobao listing or transactions fees. Taobao is the largest online shopping marketplace in China.
Tmall.com spun off from taobao.com in 2008 to connect higher-end brands with consumers. Merchants are charged a fee to list on Tmall as well as a sales commission and advertising fees. Tmall.com is where you will find brand like Nike, Gap, Marc Jacobs and Hugo Boss selling to Chinese consumers.
Source: Statista
Alibaba.com Alibaba.com is a business-to-business website which launched in 1999, as Alibaba’s first business. It is a wholesale marketplace where manufacturers, trading companies and resellers trade goods in large quantities. Buyers and suppliers from over 190 countries around the world use the site. Alibaba.com generates revenues through advertising fees as well as by charging a fee to list on the platform.
Overall Alibaba has an asset light business model where it provides an eCommerce platform to sellers looking to reach consumers. Then sellers ship merchandise directly to customers via third party logistics providers. In contrast Amazon has built and owns a vast logistics network. Within the last several years, however, Alibaba has ventured into bricks and mortar retail with its New Retail Strategy which you can read more about here.
Some of Alibaba’s other businesses include:
Alipay. Alibaba created China’s most popular digital wallet in 2003 to resolve issues of trust in the payment process between buyers and sellers. Alipay has more than one billion users and is the largest online payment platform in the world, much larger than PayPal.
AliExpress. Launched in 2010 AliExpress is a global retail marketplace. It offers products at wholesale prices and targets overseas consumers many of which live in Russia, Brazil and the United States.
Hema grocery stores. Alibaba opened its own chain of grocery stores called Hema in 2015. Alibaba has more than 250 of these grocery stores in China
Cloud computing. Alibaba provides a number of cloud computing services including networking, security, analytics and big data. Alibaba’s cloud computing business is the market leader in China.
Cainiao. Co-founded in 2013 Cainiao is Alibaba’s logistics arm. It aims to deliver merchandise in China within 24 hours and anywhere in the world in 72 hours. Alibaba owns 63% of Cainiao. “Alibaba did not originally build out a massive logistics network when it started up in e-commerce, preferring the higher-margin pure marketplace model while leaving delivery to third parties. Cainiao was a joint venture founded in 2013 that provides data and technology solutions to third-party carriers, increasing their efficiency and scale,” said The Motley Fool.
Source: Investopedia
Do you like this content? If you do subscribe to our retail trends newsletter to get the latest retail insights & trends delivered to your inbox
Sources
https://www.statista.com/statistics/225614/net-revenue-of-alibaba/
https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/121714/how-does-alibaba-make-money-simple-guide.asp
https://service.alibaba.com/buyer/faq_detail/12320786.htm
https://techcrunch.com/2018/05/04/alibaba-beats-forecasts-with-61-growth/
https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20180409005488/en/Alibaba-Cloud-Expands-Turkey
https://www.emarketer.com/Article/Alibaba-Predicts-Huge-Revenue-Growth/1015998
http://fortune.com/2018/01/19/amazon-profits-advertising/
http://about.tmall.com/tmall/fee_schedule
https://www.emarketer.com/Article/Alibabas-Tmall-Maintains-Ecommerce-Lead-China/1016432